
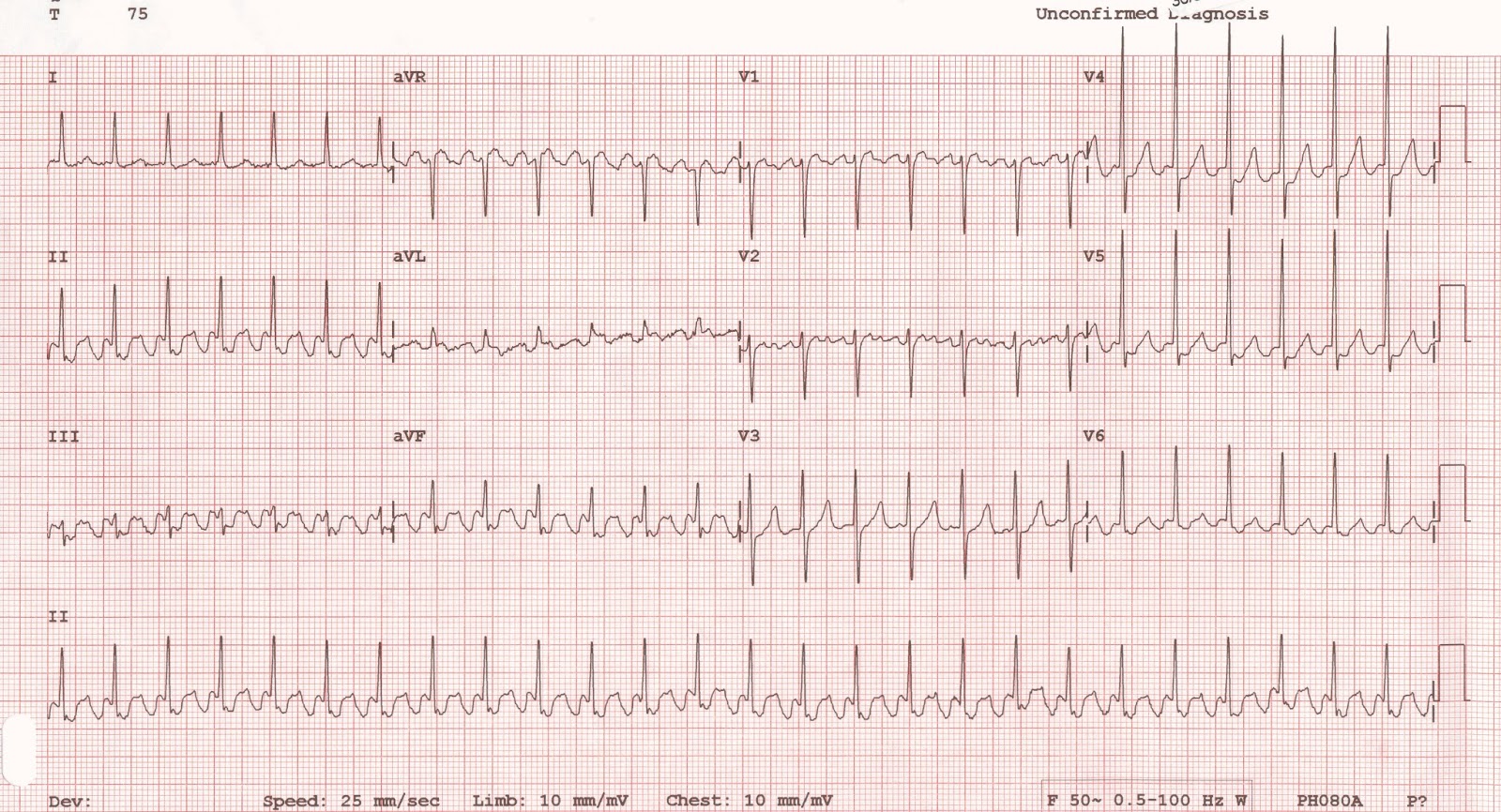
Injured heart muscle cells leak enzymes, namely cardiac troponin. Taking the time to review the clinical criteria and reporting for myocardial injuries will help inpatient coders accurately report these diagnoses.Īt the most basic level, myocardial injury refers to injury of the muscle cells of the heart. While “myocardial ischemia” is a familiar term to CDI professionals and inpatient coders, the term “myocardial injury” does not share the same widespread recognition. ~ The Fourth Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction (2018) , Doctors diagnose af using family and medical history, a physical exam, and a test called an electrocardiogram (ekg), which looks at the electrical waves your heart makes.“The clinical definition of myocardial infarction denotes the presence of acute myocardial injury detected by abnormal cardiac biomarkers in the setting of evidence of acute myocardial ischemia.” In many patients, it can also cause chest pain, heart attack, or heart failure. palpitations - an abnormal rapid heartbeatĪf can lead to an increased risk of stroke.The cause is a disorder in the heart's electrical system.often, people who have af may not even feel symptoms. Atrial fibrillation (af) is the most common type of arrhythmia. An arrhythmia is a problem with the speed or rhythm of the heartbeat.An arrhythmia in which minute areas of the atrial myocardium are in various uncoordinated stages of depolarization and repolarization instead of intermittently contracting, the atria quiver continuously in a chaotic pattern, causing a totally irregular, often rapid ventricular rate.It is caused by abnormal impulse generation In such case, blood cannot be effectively pumped into the lower chambers of the heart (heart ventricles). Abnormal cardiac rhythm that is characterized by rapid, uncoordinated firing of electrical impulses in the upper chambers of the heart (heart atria).On the ecg it is described by the replacement of consistent p waves by rapid oscillations or fibrillatory waves that vary in size, shape, and timing, associated with an irregular, frequently rapid ventricular response when atrioventricular conduction is intact. Instead of intermittently contracting, the atria quiver continuously in a chaotic pattern, causing a totally irregular, often tachycardia ventricular rate. A supraventricular arrhythmia characterized by uncoordinated atrial myocardium activation due to multiple reentry circuits with consequent deterioration of atrial mechanical function.On the ecg it is described by the replacement of consistent p waves by rapid oscillations or fibrillatory waves that vary in size, shape, and timing, associated with an irregular, frequently rapid ventricular response when atrioventricular conduction is intact The rhythm disturbance originates above the ventricles A disorder characterized by a dysrhythmia without discernible p waves and an irregular ventricular response due to multiple reentry circuits.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
